Redirects
A redirect is the automatic redirection of users and search robots from one URL to another. When a user clicks a link or enters an address into the search bar, the browser automatically opens another page, to which the redirect is configured. For example, when going to site.ru/page1, the user can be redirected to site.ru/page2.
What is a redirect used for?
There can be a multitude of reasons as to why a redirect can be useful for a site, here we’ll go through a few of those reasons, if you would like more information you can also visit Google's guide on processing redirects, where experts answer the most common questions.
- Moving a site from one address to another. If your company has changed its name, the specifics of its activities, or simply moved the site to another domain then a redirect is needed from the old domain to the new one so that those still visiting the old site are successfully directed to the new one, saving your traffic, conversion rate and profit accordingly.
- Domain gluing. This is when a site without www. Is redirected to an address with www. or vice versa, this helps search engines understand which site address is the main one.
- If a page containing valuable information is temporarily unavailable. For example, say you have ceased to produce one of your primary items on your website, but you have another closely related product, using a redirect to this replacement item means that you will not have dead links across the internet to the original product page that are potentially stopping customers from being able to access your product, the redirect will mean users still find a similar product on your site.
- When you need to eliminate exact duplicate pages on your site, and you can’t use rel = "canonical" for technical reasons.
- When you change the address of a site page (for example, after renaming it). As the old address will be saved in the search engine for some time, set up a redirect to the new address for users to visit it.
Types of redirects
There are several options for redirects, each of which has its purpose. Most often, optimizers and programmers use 301 and 302 redirects. But there are other types of redirects programmers use less frequently:
- 300 - Means multiple-choice and is used if the browser needs to redirect the user automatically. As a rule, it is used when it is necessary to select the desired language or encoding.
- 301 - Permanent redirect. It is used when it is necessary to move the page permanently. At the same time, old URLs disappear from the search results, and new ones begin to be indexed. You can view Google's redirect guide here.
- 302 - Temporary redirect. It is used when you need to temporarily redirect from one page to another. In this case, the index will contain the old page with all its inherent parameters, such as TCI and link weight.
- 303 - Used when using GET parameters on the page. It is needed to prevent pages that contain information for one-time use only from being updated.
- 304 - When the user reloads the page, it downloads data from the browser cache to the URL. It is used when the content on the page remains unchanged.
- 305 - Forwarding to a proxy server.
- 306 - Redirect is not used at the moment.
- 307 - Temporary redirect. In essence, it is similar to a 302 redirect.
How do I find pages with a redirect on Labrika’s dashboard?
You can find the corresponding report in the left menu, in the section "Technical audit" -> "Redirects."
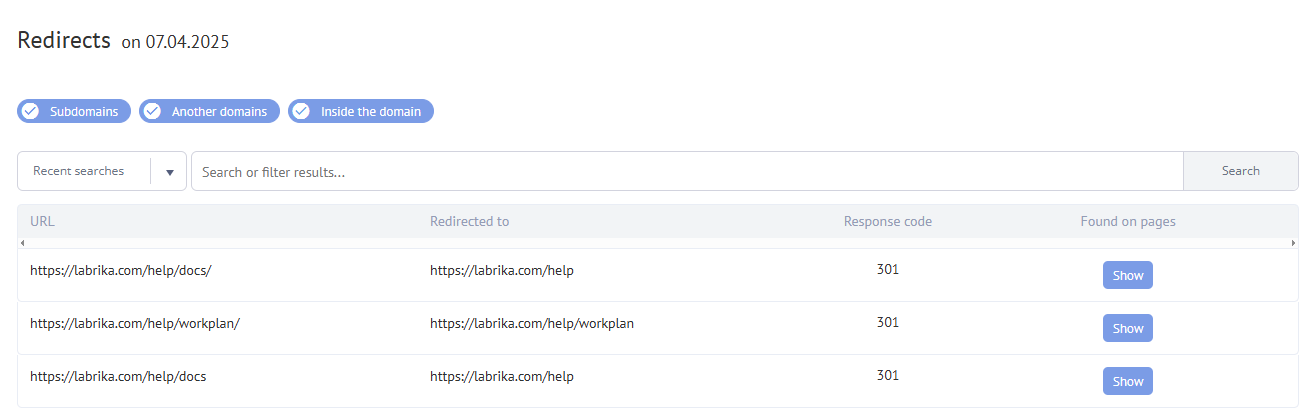
Content of the report
- The URL from which the redirect is coming.
- The URL to redirect to.
- The response code is given by the server (type of redirect).
- Title (title of the page).