All Images
Great on-page SEO involves paying attention to relatively minor features and attributes of a page’s many elements. Your objective is to provide the search engine crawler with as much valid relevant information as possible so that your page achieves a high ranking on SERPs.
It’s a game of multiple small gains, where the sum of your efforts and attention to detail gives you that vital 1% or 2% edge on your competition. That is all it may require in cases where competing pages are roughly equivalent.
Never forget that Google strives mightily to deliver the best results for its users. Your task is to ensure that your web pages do all in your power to be the best that they can be, keep Google happy, and win that all-important edge on competitors’ pages.
This tutorial is aimed at novice SEO level and focuses on one of most frequently overlooked areas for SEO – optimizing your images. We explain its importance, which attributes are most important for search engine optimization, and how to work with images to obtain the best SEO results.
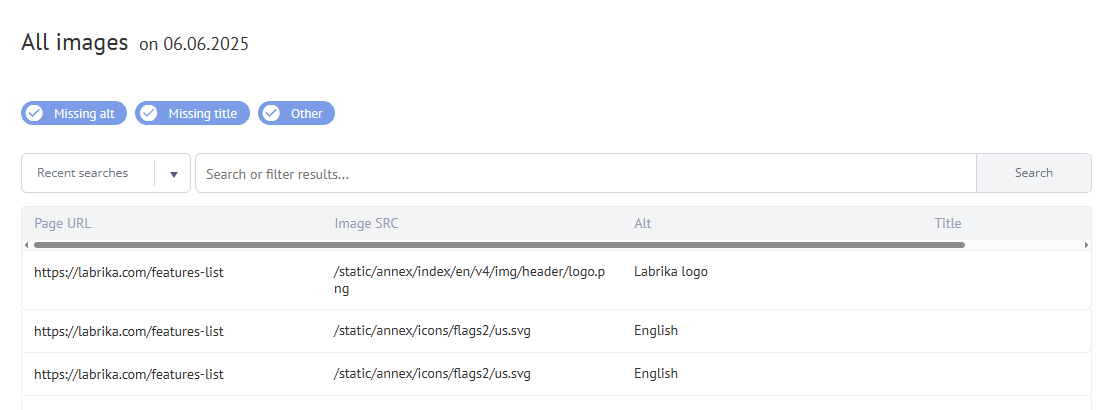
What the report shows
The syntax of the HTML <img> tag is like this example:
<img src="/products/brown-hiking-boots.png" alt="Men’s waterproof hiking boots light brown" title="Brown Hiking Boots"/>
Note: The HTML image tag can contain several additional attributes that are optional but it is vital to include the ALT text and it’s best practice to include a title too.
The Labrika optimization assessment report show you these details for each image.
- The URL of the page
-
SRC image – the file path to the image (source)
-
ALT tags/attributes (alternative text) describe an image’s content and context on your page. If there is a problem displaying the image then the ALT text appears in its place to help describe the missing image and keep the page user friendly. This text also appears when visually impaired users deploy screen readers. It makes sense to take care when crafting ALT texts. They are also assessed by web crawlers. It is the most important piece of image metadata.
-
Title - This is not as important as ALT text because it only appears when a user hovers over an image(mouse-over) when it is displayed in a little pop-up box (tooltip). Screen readers also display it. While ALT text has SEO implications, opinions are divided as to whether or not the image title has any SEO value. Its primary importance lies in keeping your pages user-friendly and encouraging user engagement.
How does ALT text impact SEO?
A search engine crawler will encounter an image on your page and will want to know more about it. This is where the ALT text performs a vital SEO role.
In fact, if you do not take care to specify ALT text, it can have a negative impact on your page ranking.
The alt tag is not really a tag but rather an attribute inside the <IMG> tag. It provides the crawler with information about the image so that it can be indexed correctly and accurately. It adds more context to the crawler’s understanding of what your page is about. Therefore it performs a vital SEO role.
It is important for Google Image Search and that is part of the reason why it is a factor in page ranking.
In fact, images are so important that you need to pay special attention to optimizing them. Pages of text are boring without images and users tend to quickly abandon them. When you include them (as you should do) it pays to ensure that they meet all the requirements to keep both Google and your site visitors happy.
9 Actions to Optimize your Images for Great SEO
-
Write good ALT tags – that is the most important step
-
Always resize images for optimal loading speed – use free online tools like this one
-
Use unique images if possible – stock images are OK but will be found on many other websites too.
-
Make sure the images and page content make sense together
-
Optimize image file names to be easily readable and include a good keyword
-
Add captions to images because they too form part of the page’s content
-
Create structured data for your images so they can be displayed as rich result snippets by Google (see Google advice for this)
-
Write good image titles that make sense for users and for SEO
-
Make the best use of your site map so that crawlers find all of your images
How to maximize your exposure in Google Images – and why you want to do this
What we described above is generic SEO for images – things you should be doing now to improve your website’s page rankings.
Next we turn our attention to Google Images, which can become a significant source of traffic when you fine-tune your content to meet its requirements.
What optimizing for Google Images can do for you
Here are the three most important benefits of targeting Google Images and which make it worthwhile to hone your skills to meet its strict requirements:
-
Increase the chances that your images will go viral
-
Drive more traffic to your website
-
Make your site load faster for a better user experience
We know that people are attracted to images. In fact, Google’s image search capability is now responsible for a large number of user searches. You want your images to be indexed by search engine web crawlers and found by searchers who will want to click through on them to your site. Therefore they need to achieve good rankings.
So what does Google demand?
How do you optimize your images and website for Google Images?
-
Delivering a great user experience is still the #1 objective
-
Ensure the image is relevant to the page’s content
-
Optimize image placement co that images appear beside, under or over relevant text content. Often it makes sense to position the most important image near the top of the page.
-
Optimize your website and images for fast loading
-
Review your page titles and descriptions to ensure they provide good SEO
-
Images should have descriptive captions, titles, and ALT text
-
Use descriptive file names (may contain a keyword – separate words with a hyphen or underscore). Google scans the path and file name in the image’s URL when assessing images.
-
Use high quality photos but ensure they are compressed before you upload them
-
Add structured data so that your pages and images show up attractively in SERPs
-
Utilize semantic markup with your images
-
Set up an image sitemap
Provide good context: Make sure that your visual content is relevant to the topic of the page. We suggest that you display images only where they add original value to the page. We particularly discourage pages where neither the images or the text are original content.
Ensure the image is relevant to the page’s content
Optimize image placement co that images appear beside, under or over relevant text content. Often it makes sense to position the most important image near the top of the page.
Some steps are relatively easy and significantly improve page load times:
-
Resize your images to the actual size they are displayed on the page rather than forcing the user's browser to resize them
-
Convert images to an efficient image format – all formats have pros and cons
-
Faster servers reduce page load times too. Consider a CDN for faster image delivery.
Use the valuable information in your Labrika toolset – it is SEO gold dust
Some relevant Labrika SEO Report stats: The tool has detected approximately 340 million SEO errors on the 69,000 or so sites it has analyzed up to mid-2022. That equates to an average of almost 5,000 errors per website (some sites are very big).
What that means is that you have an extremely efficient tool at your disposal that will do most of the heavy lifting for SEO inspection and reporting.
Your task is to interpret the data and take appropriate action. Doing so is guaranteed to improve Google's opinion of your website and you are likely to see it rise in the rankings.
How to use the Labrika SEO Report for best image SEO results
The “All images” report is located in the “Technical audit” item on the left-hand menu. It itemizes the ALT and Title attributes of your site’s images.
In general, there are two types of image: informative and decorative. Decorative images are things like icons, borders, corners and graphics that merely make the site more attractive. Informative images are the important ones that convey information to the user – such as your photos, infographics and so on.
-
Ignore decorative images for SEO purposes
-
Find images with missing ALT text and create ALT content.
-
Review the size of each image and try to match its dimensions to its size on the page. Compress large images but always maintain a high quality.
-
If possible substitute unique images for stock images so that your website is the master copy of those images.
-
This may take time but approach it in a methodical manner and see it through to the end.
Best practices for creating ALT texts and Titles for images
Add ALT text all non-decorative images. Keep it short and descriptive, like a tweet. Don't say things like “image of” or “photo of”. Cut to the chase and describe what is happening in the image.
How to write great ALT tag text
The primary purpose of this image attribute is to help users. Readers with visual impairment want to get the same benefit from visuals like charts and photos that fully sighted readers get. So do web crawlers as it happens!
Write your text with visually impaired people in mind. Certainly add one or two keywords of course for SEO purposes but ensure the information really does describe what is happening in the image. Importantly, do not stuff it with keywords.
For example, rather than saying “brown boot” you might say “a hiker wearing brown boots on the trail.”
It makes good sense to get into the habit of adding ALT text to every image you publish on your website. That makes this aspect of SEO almost an automatic and instinctive action that takes maybe one or two minutes at most. If you have not been doing it already, then set aside the time to comb methodically through your website and ensure all images have good descriptive ALT text.
Useful tips for writing ALT tag copy
All non-decorative images must have ALT text that accurately describes them.
Users with weak vision who have to enlarge the screen depend on ALT text, which usually scales better than images do.
-
Keep it short and to the point, like a Tweet. As a rule of thumb, keep it to less than 125 characters. Screen readers or platforms may truncate anything longer than that. If a visual really does need longer explanatory text, you can use the "longdesc" attribute of the <IMG> tag to link to a different page.
-
Describe the content of the image objectively (don’t editorialize)
-
Don’t state the obvious, so avoid beginning with things like “photo of …” or “picture shows …”
-
Do use one or two keywords but keep the human user in mind at all times, not search engines
-
If an image contains text, then write that text also in the ALT tag. That way visually impaired users will better understand the image
-
Avoid repeating yourself
Finally
Search Engine Optimization is an ongoing task. To do it properly you should draft a schedule of routine monitoring and tweaking to maintain your website’s images, content and performance to the standards that Google demands.
Find out more about image SEO at Google Images best practices.
For further reading, you can start with Google’s SEO Starter Guide.
