Ads
Paid traffic refers to the visitors who arrive at your website through online advertisements that require payment. This type of traffic is essential for many businesses looking to increase visibility and reach a broader audience. The primary methods for generating paid traffic include contextual advertising and targeted advertising on social media platforms.
Contextual advertising is a form of paid online advertising where the advertisements displayed are relevant to the user's current search query, the content they are viewing, or the specific webpage they are on. This strategy is particularly effective for attracting potential customers because the ads are tailored to align with what users are actively interested in or searching for. For instance, if a user is browsing a website about fitness, they may encounter ads related to gym equipment or health supplements.
An excellent example of contextual advertising is Google Ads, which utilizes Google AdWords to deliver contextually relevant advertisements based on user behavior and search patterns. This method helps businesses increase site engagement by presenting their offerings to users who are likely to be interested, thus improving landing page metrics.
On the other hand, targeted advertising through social media networks focuses on delivering ads based on specific user demographics, such as age, gender, location, and interests. This means that even if a user is not actively searching for a product, they may still see ads for it while browsing their social media feeds. This approach allows businesses to reach their target audience effectively, increasing the chances of conversion and user retention.
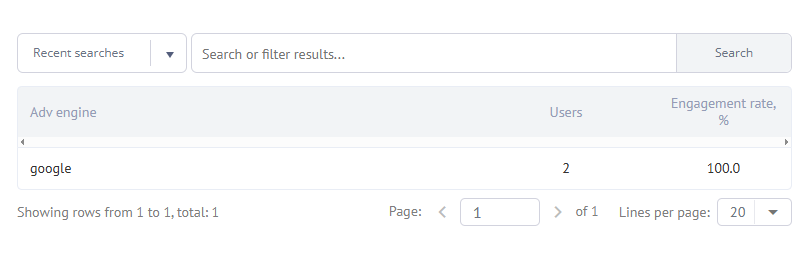
Labrika's Paid Traffic report provides valuable insights into the performance of different advertising channels by presenting data on user visits and bounce rates. This report is an essential tool for analyzing the effectiveness of your paid advertising campaigns.
Utilizing the Paid Traffic Report
To make the most of the Paid Traffic report, you first need to connect your Google Analytics account to Labrika. Once this integration is complete, you can access critical information, including:
- The source of your advertising traffic, detailing the system and channel through which users arrive at your page (e.g., Facebook, Google, etc.).
- The total number of users visiting your site from each source, allowing you to gauge which channels are most effective.
- The percentage of bounces from the total visits originating from a given source. A bounce occurs when users leave a page quickly after clicking on it, indicating a lack of engagement.
- The number of lost users, which refers to users who have stopped interacting with your site altogether.
Any metrics that fall outside of normal ranges are highlighted in red, making it easy to identify areas that require attention.
Assessing Ad Campaign Effectiveness
This report is crucial for evaluating the overall effectiveness of your advertising campaigns, helping you minimize waste in your ad budgets. For example, if certain sources show low traffic, high bounce rates, and a significant number of lost users, it indicates that these channels are ineffective and not providing a good return on investment. By analyzing this report, you can adjust your budget to focus on channels that yield better results.
Here are some adjustments you might consider making based on the report's insights:
- Adjust bid sizes: Ensure that your bid amounts are sufficient to secure enough impressions and traffic, particularly in competitive markets. This strategy is essential for maximizing your visibility.
- Set up targeting: Tailor your ads to attract your ideal audience. Focus on the interests of the largest group of loyal users; the broader your targeted audience, the lower your bounce rate is likely to be. Additionally, refine your regional targeting to reach users more effectively.
- Create compelling ads: Incorporate relevant keywords in your headlines and develop a unique selling proposition (USP) that clearly communicates the primary benefits of your products or services to your target audience. Emphasize your competitive advantages such as free shipping, a wide selection of products, low prices, and warranties. Including information about discounts, promotions, and sales can significantly enhance the attractiveness of your ads.
- Review your ad content: Ensure that your ads are well-written and free of spelling or grammatical errors. Misleading headlines or poorly constructed text can undermine user trust and lead to higher bounce rates.
- Utilize engaging visuals: Incorporate quick links, eye-catching images, and add-ons in your ads to capture user attention and encourage interaction.
- Link to relevant landing pages: Each ad should direct users to a landing page that provides comprehensive information about the advertised product or service. This alignment is crucial for improving landing page conversion rates.
- Optimize for mobile devices: Given the increasing number of users accessing websites via mobile, it is essential to ensure that your ads and landing pages are responsive and user-friendly on all devices.
Improving User Experience and Reducing Bounce Rates
To enhance your website's performance and minimize bounce rates, consider implementing the following user experience improvements:
- Optimize loading speed: A slow-loading page can significantly impact user retention. Use tools to analyze your page load times and implement changes to minimize delays, ensuring users can access your content quickly.
- Enhance navigation: A clear and intuitive navigation structure helps users find what they are looking for without frustration. Consider simplifying your menus and ensuring that all links are functional.
- Use engaging content: High-quality content that resonates with your audience can keep users on your site longer. Incorporate informative articles, engaging videos, and interactive elements to captivate users and encourage them to explore further.
- Implement A/B testing: Experiment with different versions of your landing pages to identify which elements resonate best with your audience. This data-driven approach can help you refine your strategies and boost conversion rates.
- Monitor user feedback: Pay attention to user feedback and reviews to understand pain points and areas for improvement. This feedback can be invaluable in refining your website and increasing user satisfaction.
Analytics and Metrics for Tracking Performance
Utilizing analytics is crucial for understanding your website's performance. Key metrics to monitor include:
- Bounce Rate: This metric indicates the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate can signal issues with your landing pages or the relevance of your content.
- Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter. Improving landing page conversion tactics can lead to higher conversion rates.
- Traffic Sources: Analyze where your traffic is coming from to determine which channels are most effective. This information can guide your advertising strategies and budget allocation.
- User Engagement: Track metrics such as average session duration and pages per session to gauge how engaged users are with your content. High engagement levels often correlate with lower bounce rates.
Strategies for Effective User Retention
Retaining users is as important as attracting new ones. Here are some effective user retention strategies:
- Build a community: Engage your users by creating forums, social media groups, or newsletters where they can interact and share experiences. This fosters a sense of belonging and loyalty.
- Offer personalized experiences: Use data analytics to tailor content and offers to individual users based on their preferences and behavior. Personalization can significantly enhance user satisfaction and retention.
- Implement loyalty programs: Reward returning customers with discounts, exclusive offers, or points that can be redeemed for future purchases. This encourages repeat business and strengthens customer loyalty.
- Provide excellent customer service: Ensure that your customer service team is responsive and helpful. Addressing user concerns promptly can enhance trust and encourage users to return.
- Regularly update content: Keep your website fresh by regularly adding new content, products, or features. This not only attracts new visitors but also encourages existing users to return for new experiences.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing paid traffic is crucial for enhancing your website's performance. By leveraging analytics to monitor bounce rates, traffic sources, and user engagement, you can make informed decisions that lead to improved landing page metrics and increased site engagement. The strategies discussed here can help reduce bounce rates and foster effective user retention, ultimately driving growth and success for your business.
By continuously optimizing your advertising campaigns and focusing on user experience improvements, you can create a robust online presence that not only attracts new visitors but also keeps them engaged and returning for more. Remember, a happy user is likely to become a repeat customer and advocate for your brand.
As you implement these strategies, keep in mind that the digital landscape is ever-evolving. Staying informed about industry trends and adapting your approach accordingly will help you maintain a competitive edge. Regularly review your analytics to track the effectiveness of your campaigns and make necessary adjustments to your strategies.
In summary, paid traffic is a powerful tool for driving users to your website, but its effectiveness hinges on your ability to analyze and optimize every aspect of your advertising efforts. By focusing on reducing bounce rates, improving landing page performance, and enhancing user experience, you can significantly increase site engagement and foster effective user retention. Utilize the insights gained from analytics to inform your decisions, and remember that the ultimate goal is to create a seamless and enjoyable experience for your users.
As you embark on this journey, leverage the resources available through tools like Labrika to streamline your SEO efforts and maximize your website's potential. With the right strategies in place, you can transform your paid traffic into a valuable asset that drives growth and success for your business.
For more tips and insights on optimizing your website and improving user engagement, explore our additional resources and articles. Your path to enhanced website performance starts here!
